Sequins™ Metagenomics Bioinformatics Resources

Sequins Metagenomics analyses of Known and Unknown Targets.
These tutorials describe the analyses of the Sequins Metagenomics Core Control Set in two ways: (1) for Known Targets and (2) for Unknown Targets.
Bioinformatics workflow for Known Targets
Reference-Based Quantification of Known Targets
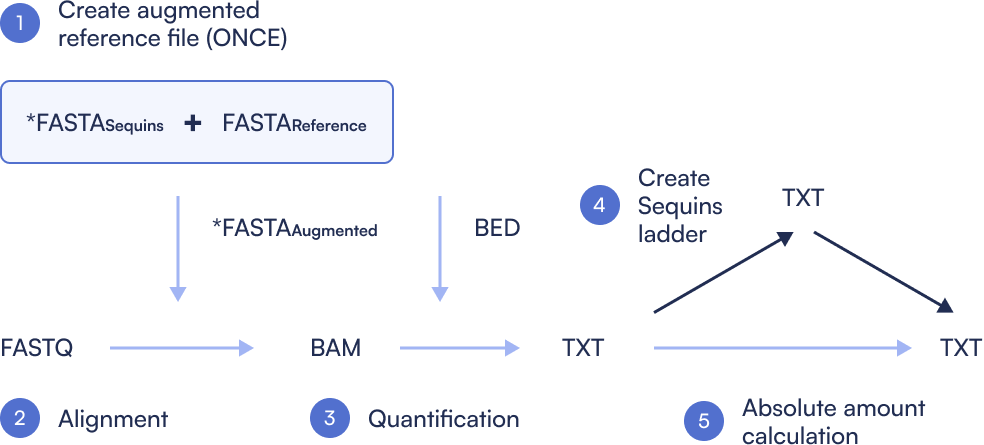
Step 1: Create Sequins augmented Reference file
Only done once. Concatenate the microbial reference genomes with the metasequin_sequences.fa file, then index the combined reference. This step ensures alignment tools can recognize both microbial and synthetic control sequences in downstream analysis.

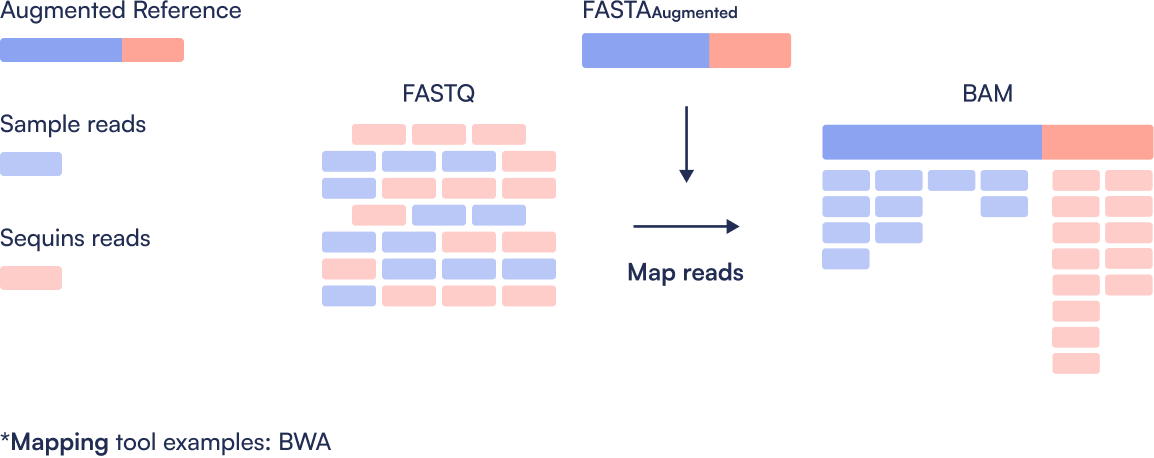
Step 2: Align
Perform quality control (e.g., trimming and filtering) on raw FASTQ files. Post-process the resulting alignments to generate sorted, BAM files ready for quantification.
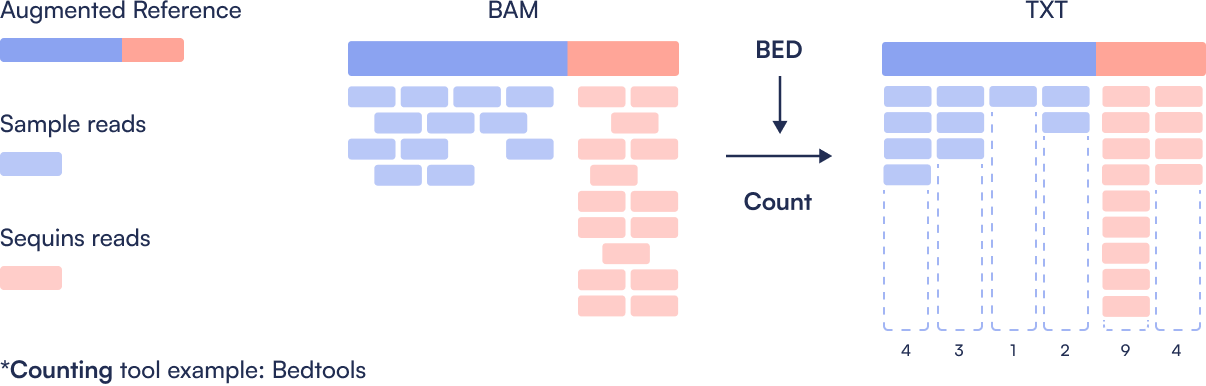
Step 3: Quantification
Count the number of reads mapping to each microbial and Sequin region. This produces a coverage table showing per-region read counts, the basis for estimating abundance.
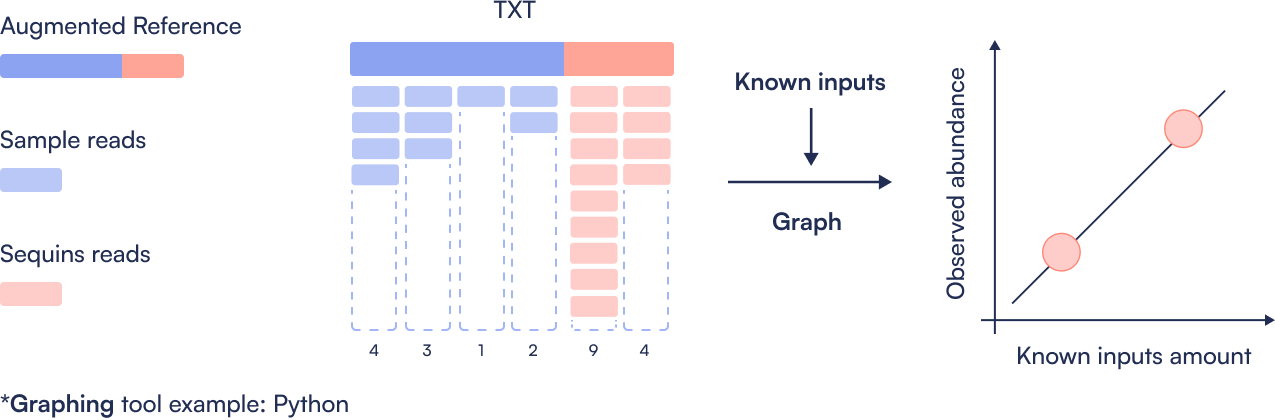
Step 4: Create Sequins ladder
Compare observed Sequin abundance (from sequencing) to expected values (from known spike-in concentrations). Generate a log-log regression plot to assess dynamic range, linearity, and performance of the metagenomics workflow.
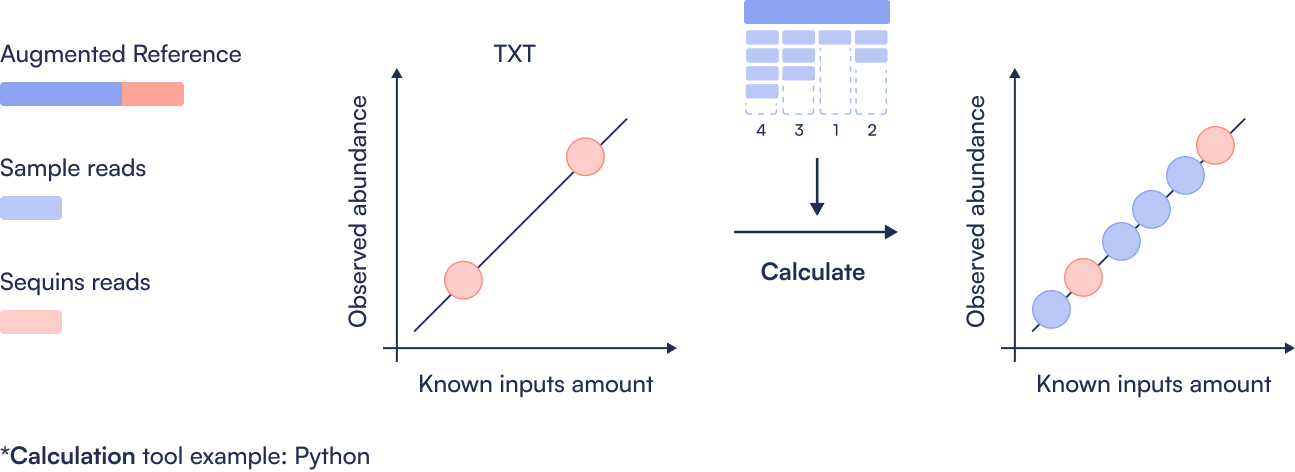
Step 5: Absolute abundance calculation
Perform linear regression between expected and observed Sequin abundances to calculate the limit of detection (LoD) and limit of quantification (LoQ). Use this calibration to convert microbial read counts into absolute concentrations, enabling precise comparisons between samples.
Tutorial for analysis of Known Targets
Here you can find an example workflow for processing short-read metagenomics sequencing data that have had the Sequins Metagenomics Core Control Set spiked in. It highlights the places where Sequins specific steps must be taken, and it is not intended as an example of a production workflow.
Reference-Based Quantification of Known Targets

FAQ - Known References (Reference-based Quantification)
When should I use this metagenomics approach?
When you’re quantifying a defined set of microbial targets (e.g., a pathogen panel, fermentation panel).
How does using Sequins impact my reference-based metagenomics bioinformatics workflow?
There is minimal impact to your bioinformatics workflow. There are two (2) minor additions to a standard taxonomic classification metagenomics bioinformatics workflow:
- An augmented metagenomics database (combination of microbial genome references and Sequins references).
- Generation of the Sequins ladder to enable assessment of sequencing performance, calculating limits of detection/quantification, and abundance quantification.
How do I create the augmented reference metagenomics file for my reference-based metagenomics bioinformatics workflow?
Simply combine your desired metagenomics genome file with the Sequins reference file. One method is to use the cat command on Unix.
Where do I get the Sequins reference file?
The Sequins team will provide you with the Sequins decoy reference file.
Why classify against an augmented metagenomics database?
We recommend integration of Sequins into your chosen taxonomic database to ensure Sequins are processed through the exact same workflow as your microbial species, providing the most comparable results. If this is not viable, a less robust option is to quantify Sequins separately through alignment against the provided Sequins reference file and merge abundance results with those obtained for the microbial species after taxonomic assignment.
What aligners are compatible with Sequins?
Sequins will minimally impact your bioinformatics workflow and are compatible with any aligner.
What quantification tools are compatible with Sequins?
Sequins will minimally impact your bioinformatics workflow and are compatible with any quantification tool.
Bioinformatics workflow for Unknown Targets
Quantification of Unknown Targets
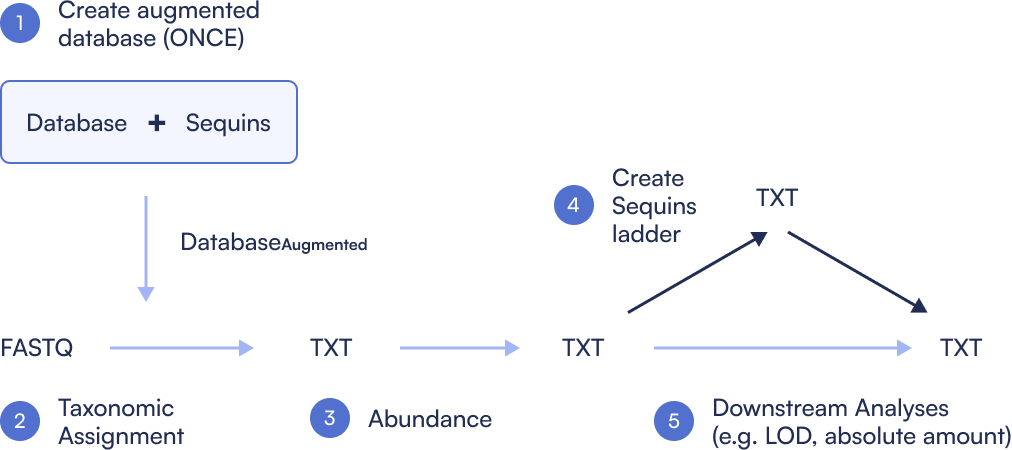
Step 1: Create Sequins augmented database
Step 2: Assign taxonomy
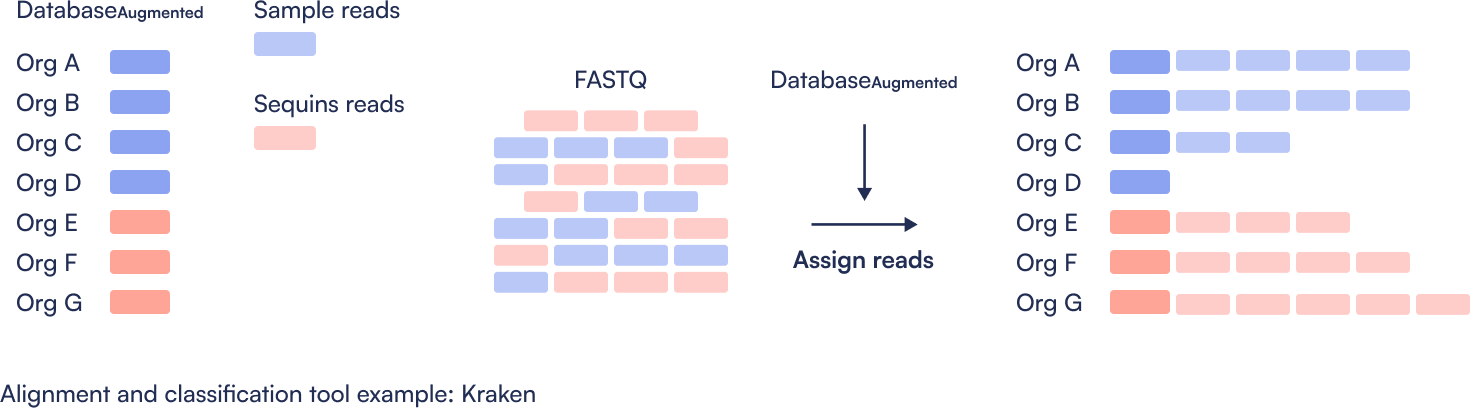
Step 3: Quantify abundance
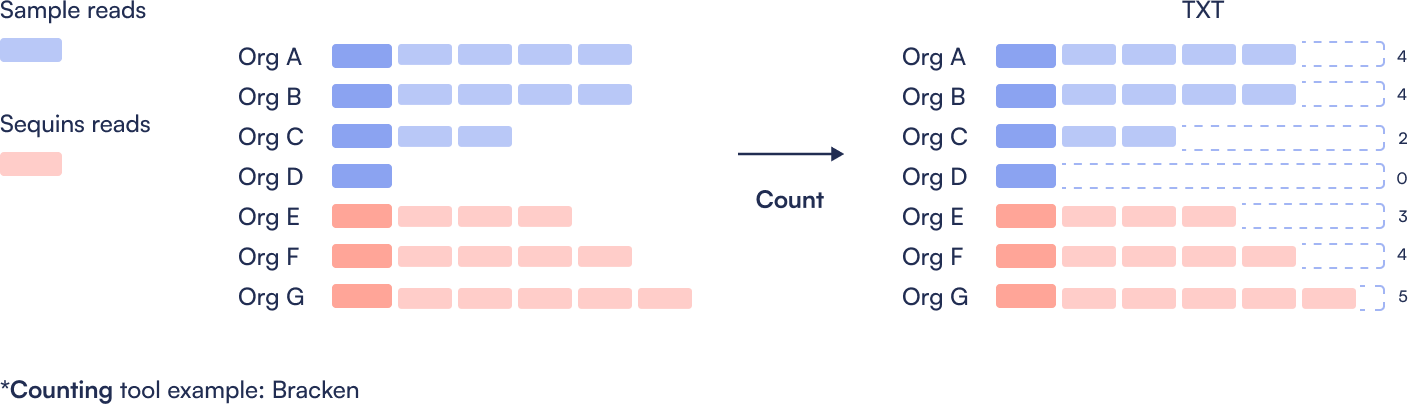
Step 4: Create Sequins ladder
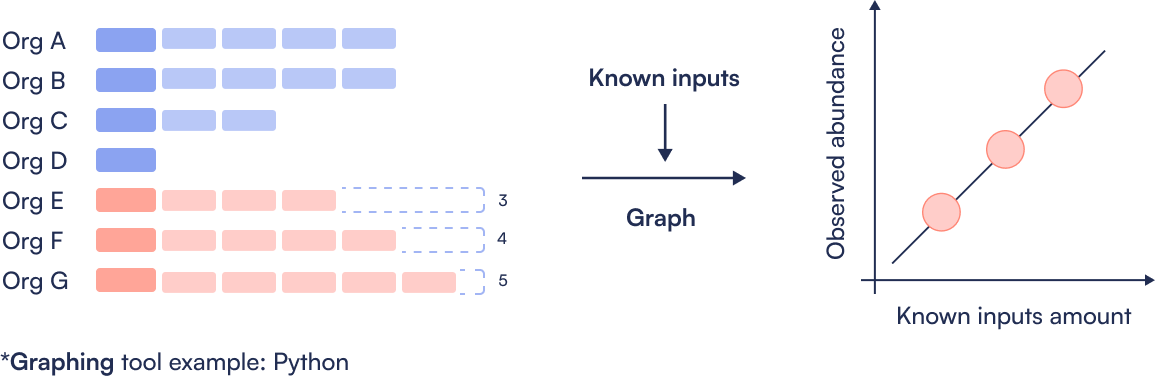
Step 5: Absolute abundance calculation
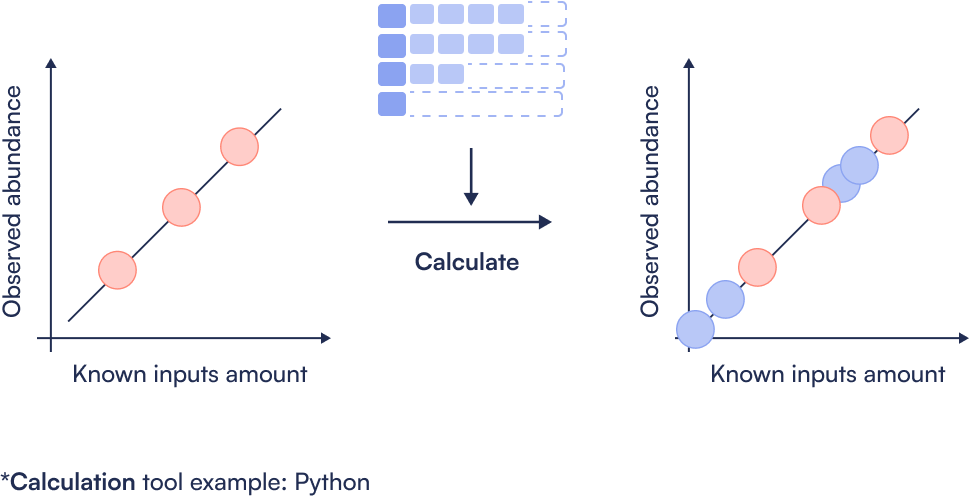
Step 6: Determine LOD
Tutorial for analysis of Unknown Targets
Taxonomic Classification and Abundance Estimation of Unknown Targets

FAQ - Unknown/Complex Communities (Taxonomic Classification)
When should I use this metagenomics approach?
When you’re doing shotgun metagenomics without a fixed target list and need to classify reads taxonomically.
How does using Sequins impact my taxonomic classification metagenomics bioinformatics workflow?
- An augmented metagenomics database (combination of microbial genome references and Sequins references).
- Generation of the Sequins ladder to enable assessment of sequencing performance, calculating limits of detection/quantification, and abundance quantification.
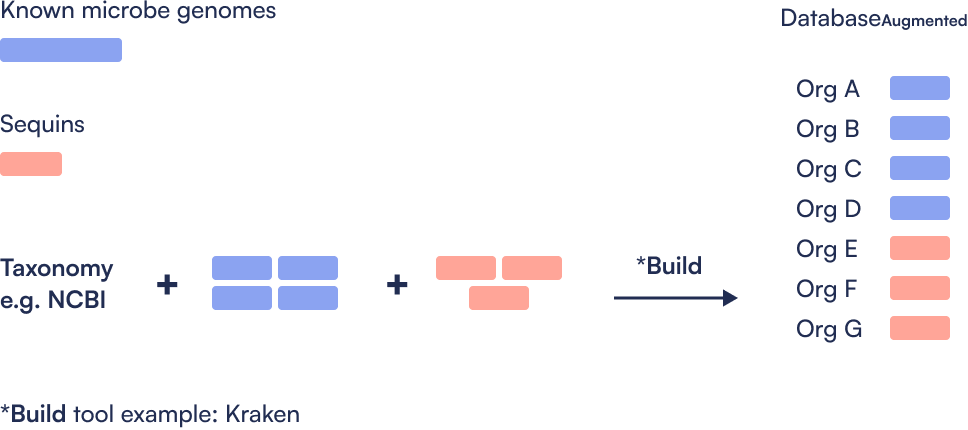
How do I create the augmented metagenomics database for my taxonomic classification metagenomics bioinformatics workflow?
You should follow the instructions from your preferred taxonomic database provider to create a custom database, but the process typically entails:
Assignment of taxonomic identifiers to Sequins.
Addition of the Sequins reference sequences into the reference files used to build the database.
Rebuild of the database.
The instructions for building a Kraken2 custom database containing Sequins can be found HERE. A pre-built custom Kraken2 database is also available upon request from the Sequins team.
Where do I get the Sequins reference file?
The Sequins team will provide you with the Sequins decoy reference file.
Why classify against an augmented metagenomics database?
We recommend integration of Sequins into your chosen taxonomic database to ensure Sequins are processed through the exact same workflow as your microbial species, providing the most comparable results. If this is not viable, a less robust option is to quantify Sequins separately through alignment against the provided Sequins reference file and merge abundance results with those obtained for the microbial species after taxonomic assignment.
What taxonomic classifiers are compatible with Sequins?
Sequins will minimally impact your bioinformatics workflow and are compatible with any taxonomic classifiers once integrated into the reference database.
What quantification tools are compatible with Sequins?
Sequins will minimally impact your bioinformatics workflow and are compatible with any quantification tool.
Request access to tutorial datasets
"*" indicates required fields