Sequins™ WGS Bioinformatics Resources

Sequins are synthetic DNA standards designed to mirror natural genomic features, enabling enhanced quality insights and improved calling confidence of whole genome sequencing (WGS) data.
As an NGS spike-in, Sequins provide internal controls for benchmarking performance across library preparation, sequencing, and data analysis. When using Sequins in WGS, key bioinformatics considerations include accurate alignment of synthetic sequences, variant calling within the spike-in reference, and comparison of observed versus expected metrics to assess sensitivity, specificity, and dynamic range.
This section provides guidance to support effective use of Sequins in your WGS workflows. If you require any further assistance, please email support@sequins.bio.
WGS Bioinformatics Workflow Overview
The diagram illustrates a five-step workflow for integrating Sequins into WGS bioinformatics pipelines, enabling robust performance benchmarking and variant calling accuracy assessment.
This structured process supports both Docker-based and independent toolchain implementations and is tailored to be flexible for diverse research and clinical applications using Sequins in WGS.
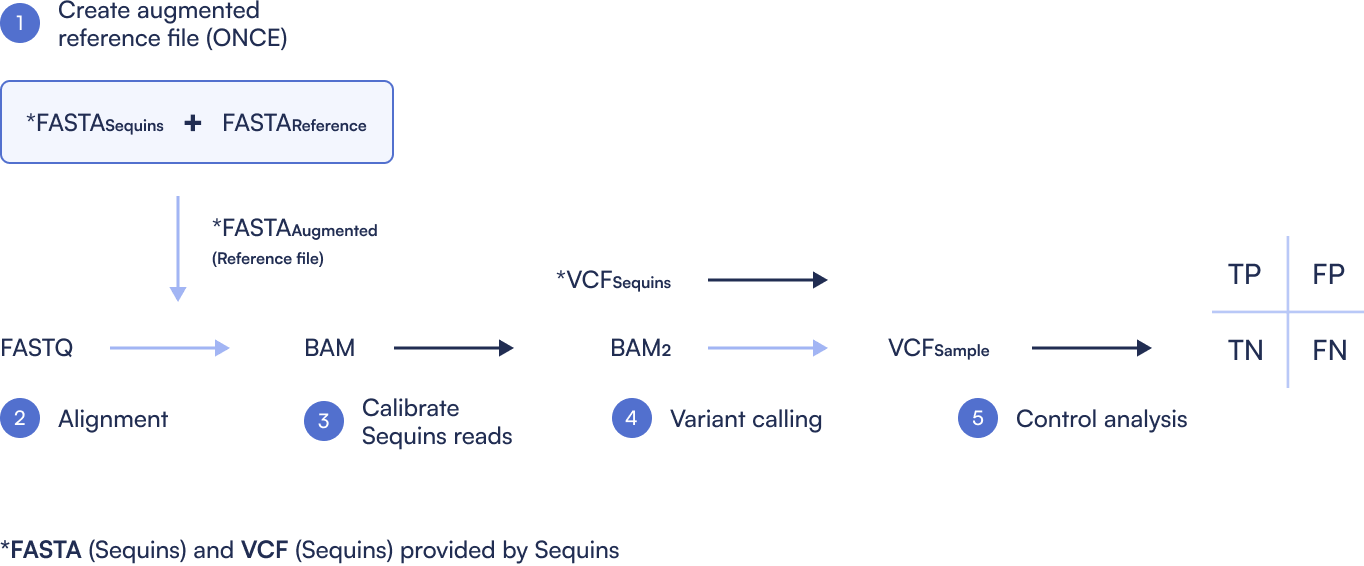
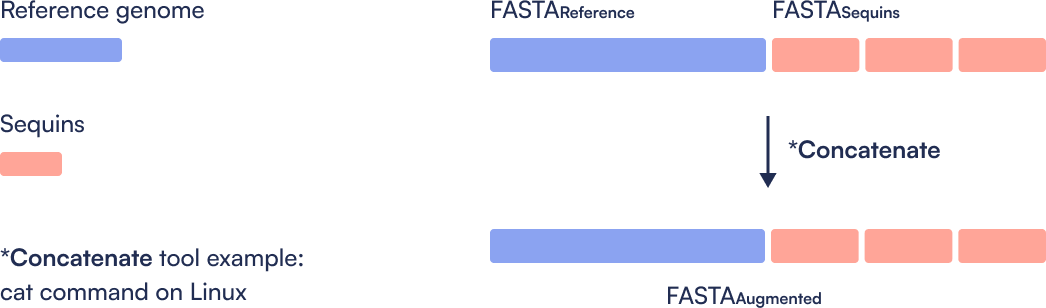
Step 1: Create Sequins Augmented Reference file
Combine the standard reference genome (e.g., GRCh38) with the Sequins decoy chromosome to generate an augmented reference. This step is performed once and used throughout the workflow.
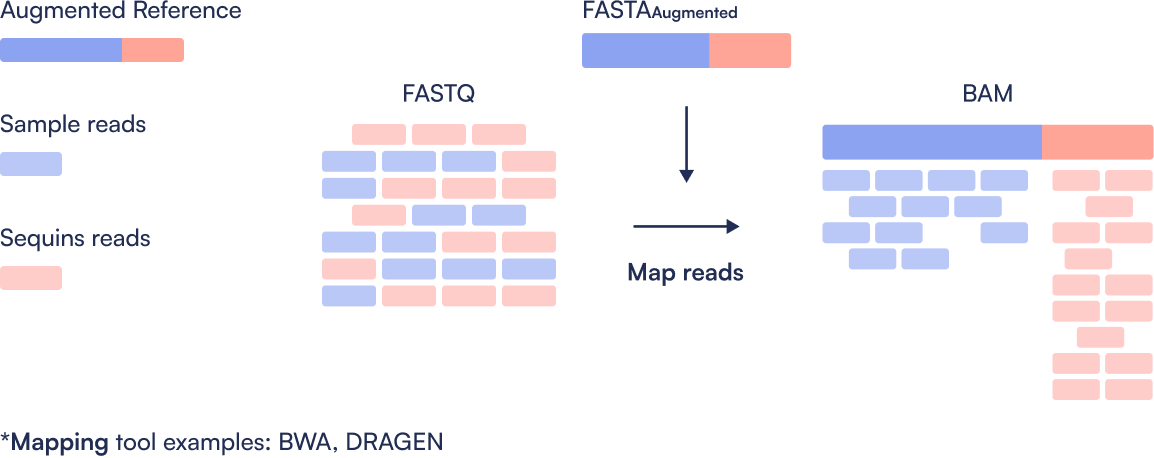
Step 2: Read Alignment
Sequence reads (FASTQ) are aligned to the augmented reference genome using a tool such as BWA, producing a BAM file that contains both sample and Sequins reads.
Step 3: Calibrate Sequins Reads
Sequins are typically sequenced at higher coverage than the sample. To ensure fair comparison, the Sequins regions in the BAM are downsampled to match the coverage of their corresponding human genome locations. This calibrated BAM file better reflects variant detection sensitivity in the actual sample.
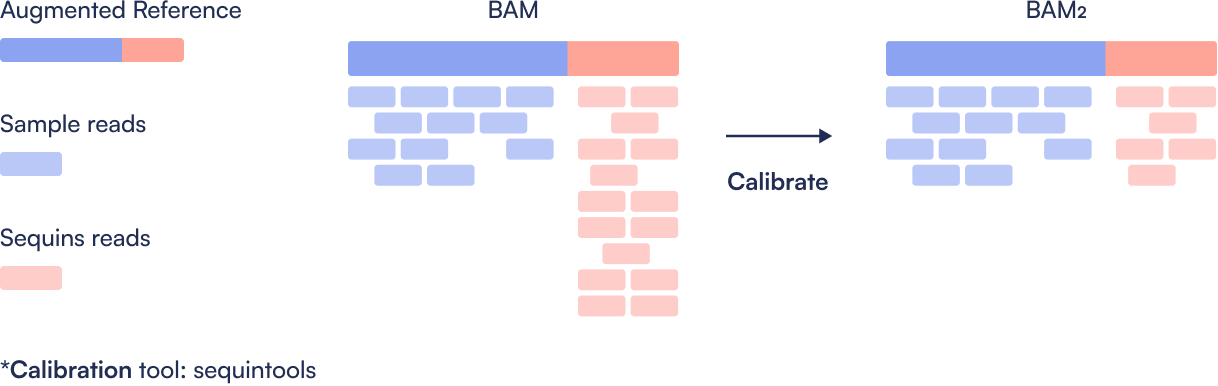
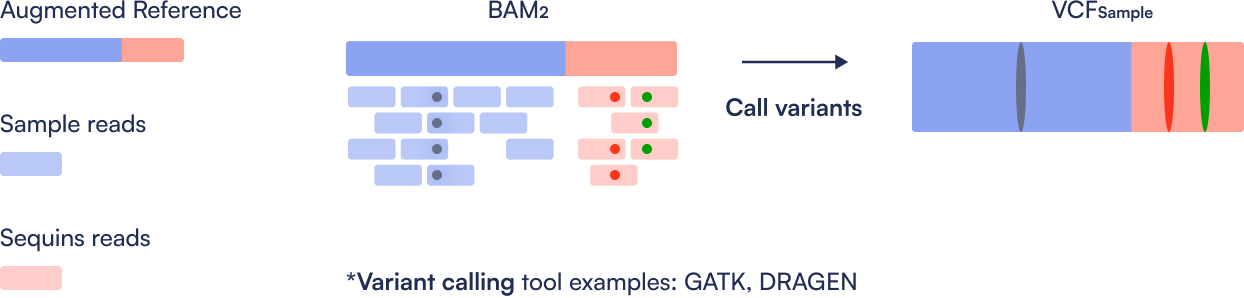
Step 4: Variant Calling
Variants are called separately on the calibrated BAM for Sequins and the sample. This step produces two VCF files: one for the Sequins controls and one for the sample.
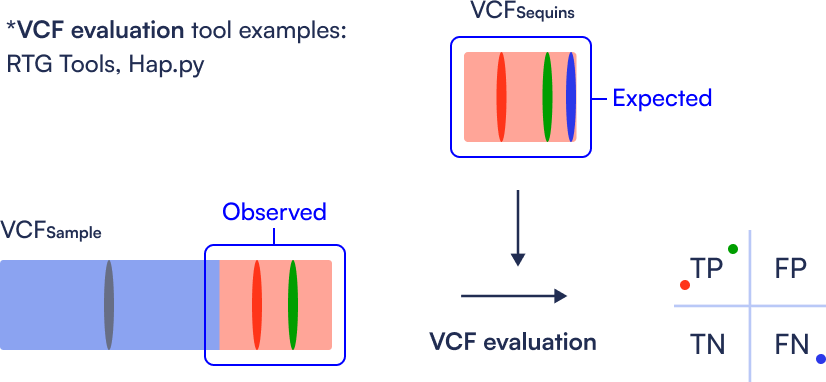
Step 5: Performance Evaluation (Control Analysis)
By comparing the known variant truth set of Sequins (VCF Sequins) to the variant calls obtained from the pipeline, users can generate precision, sensitivity, and F-measure metrics using RTG Tools. This enables identification of false positives and negatives, and provides a clear benchmark of the pipeline’s performance.
WGS Sequins Tutorial
Here you can find an example workflow for processing data that have had Sequins spiked in. It highlights the places where Sequins specific steps must be taken, and it is not intended as an example of a production workflow.
Learn more about WGS Sequins tutorial

Frequently asked questions
How does using Sequins impact my WGS bioinformatics workflow?
There is minimal impact to your bioinformatics workflow. There are two (2) minor additions to a standard WGS bioinformatics workflow:
- An augmented reference genome file (combination of standard human genome reference file and Sequins reference file).
- Integration of Sequins’ read downsampling software (sequintools) into your bioinformatics workflow.
How do I create the augmented reference genome file for my WGS bioinformatics workflow?
Simply combine your desired human reference genome file with the Sequins reference file. One method is to use the cat command on Unix.
Where do I get the Sequins reference file?
The Sequins team will provide you with the Sequins decoy reference file.
Why align to an augmented reference?
So Sequin reads align to the Sequins reference portions of the augmented reference, while sample reads align with the human reference genome portion of the augmented reference.
How do I integrate sequintools into my WGS bioinformatics workflow?
The Sequins molecules added to your sample are short sequences of nucleic acids, which will naturally accrue higher cover than other relative-sized regions in the rest of the sample. As a result, it is important to downsample the Sequins reads to be more relative to the number of reads in the rest of the sample. The downsampling step is done before variant calling. To accomplish this, simply add the sequintools docker into your bioinformatics pipeline. The sequintools docker should be compatible with standard scientific workflow managers, such as Nextflow.
Where do I get sequintools (Sequins software)?
sequintools is open source software, and it is available on GitHub: (https://github.com/sequinsbio/sequintools).
What aligners are compatible with Sequins?
Sequins will minimally impact your bioinformatics workflow and are compatible with any aligner.
What variant callers are compatible with Sequins?
Sequins will minimally impact your bioinformatics workflow and are compatible with any variant caller.
Why do the Sequins align next to each other, are they designed in one contiguous molecule?
Sequins are individual molecules, not one continuous molecule. Placing all sequences on the decoy FASTA file that is provided is purely a convenience and the Sequins can be analyzed by aligning to the individual sequences if you prefer.
Why do I see gaps between my Sequins regions?
Because the decoy FASTA is a synthetic construct and the individual Sequins are not really one continuous molecule.
Why do I see drop off in coverage at the terminal regions of each Sequins?
This is just a natural effect of sequencing to the end of a molecule. As you reach the end of a molecule there are fewer positions a read can start or end so there is a natural drop off in coverage.
I’m using Dragen, how do I incorporate Sequins?
You must concatenate the Sequin sequences to your reference and re-index in the same way for any other system.
Request access to the datasets used in this tutorial
"*" indicates required fields